(open access)
R. Wang,
T. Zhang,
P. Wang
Volume 521; Issue 1
Pages 59-62
Accepted for publication: 23.11.2015 r.
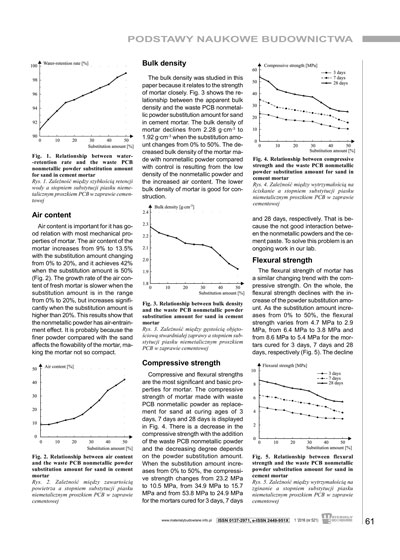
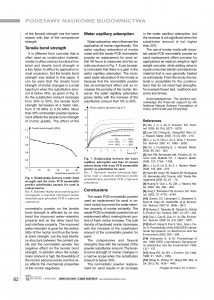
The nonmetallic powder recycled from waste printed circuit boards (PCB) is used in cement mortar as replacement for sand. The results show that the waste PCB nonmetallic powder causes an increase in air content and improves the water-retention property of fresh mortar, decreases the bulk density of hardened mortar.There is a decrease in the compressive and flexural strengths with the addition of waste PCB nonmetallic powder and the decreasing degree depends on the substitution amount of the nonmetallic powder for sand. The tensile bond strength decreases slowly with the increase of the substitution amount from 0% to 35%. The water capillary adsorption of mortar is close to that of control when 10% and 20% sand is replaced. The use of mortar made with recycled waste PCB nonmetallic powder as sand replacement offers promise for applications as medium weight or light weight concrete, while adding value to a post-consumer electric and electronic material that is now generally treated as solid waste.
- Wu J, Li J, Xu Z. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42 (14), 5272 – 5276.
- Lee CH, Chang SL, Wang KM, Wen LC. J. Hazard. Mater. 2000, 73 (3), 209 – 210.
- Li J, Lu H, Guo J, Xu Z, Zhou Y. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1995 – 2000.
- Cui J, Forssberg E. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 99, 243 – 263.
- Veit HM, Bernardes AM, Ferreira JZ, Tenorio JAS, Malfatti CF. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1704 – 1709.
- Li J, Lu H, Liu S, Xu Z. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 269 – 275.
- Veit HM, Diehl TR, Salami AP, Rodrigues JS, Bernardes AM, Tenorio JAS. Waste Management 2005, 25, 67 – 74.
- Huang K, Guo J, Xu ZM. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 399 – 408.
- Jang Y, Townsend TG. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4778 – 4784.
- Owens CV, Lambright C, Bobseine K, Ryan B, Gray LE, Gullett BK, et al. Environ. Sci. Technol, 2007 41, 8506 – 8511.
- Huang Y, Takaoka M, Takeda N, Oshita K. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 257 – 262.
- Guo J, Cao B, Guo JY, Xu ZM. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42 (14), 5267 – 5671.
- Mou P, Xiang D, Pan X,Wa L, Gao J, Duan G. Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Symposium on Electronics and the Environment 2005, 205 – 209.
- Yokoyama S, Iji M. Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Symposium on Electronics and the Environment 1995, 132 – 137.
- Hong SG, Su SH. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. 1996, 31, 1345 – 1359.
- Wang R, Zhang TF, Wang PM. Mat. & Str. 2012, 45, 1439 – 1445.
- Ru Wang, Prof. - Key Laboratory of Advanced Civil Engineering Materials of Ministry of Education; School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tongji University
- Tengfei Zhang - Key Laboratory of Advanced Civil Engineering Materials of Ministry of Education; School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tongji University
- Peiming Wang, Prof. - Key Laboratory of Advanced Civil Engineering Materials of Ministry of Education; School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tongji University
Ru Wang, Prof.